
At its core, grammar is the set of rules that helps us build sentences that make sense. It’s the blueprint for clear communication, covering everything from sentence structure and parts of speech to punctuation. For content creators, mastering these fundamentals is the first step toward writing that not only informs but also persuades.
Why Basic Grammar Still Matters in the Age of AI
With AI writing tools everywhere, you might wonder if you still need to bother with grammar. The answer is a resounding yes. AI can generate text in a flash, but it often misses the subtle nuances and authentic voice that connect with a reader. Think of it this way: grammar is the steering wheel that puts you in control of your message.
Good grammar isn't just about avoiding red squiggles; it’s about building credibility. In fact, a study found that 59% of consumers would not buy from a company with obvious grammatical errors on its website. When your writing is clean and error-free, your audience trusts what you have to say.
The Pillars of Effective Communication
A solid grasp of grammar gives you the power to be precise. It lets you break down complex ideas into simple, digestible sentences, ensuring your audience understands exactly what you mean. This skill is non-negotiable for content creators, marketers, and students who need their message to land perfectly.
This infographic neatly summarizes why strong grammar is so crucial, breaking it down into three key pillars.
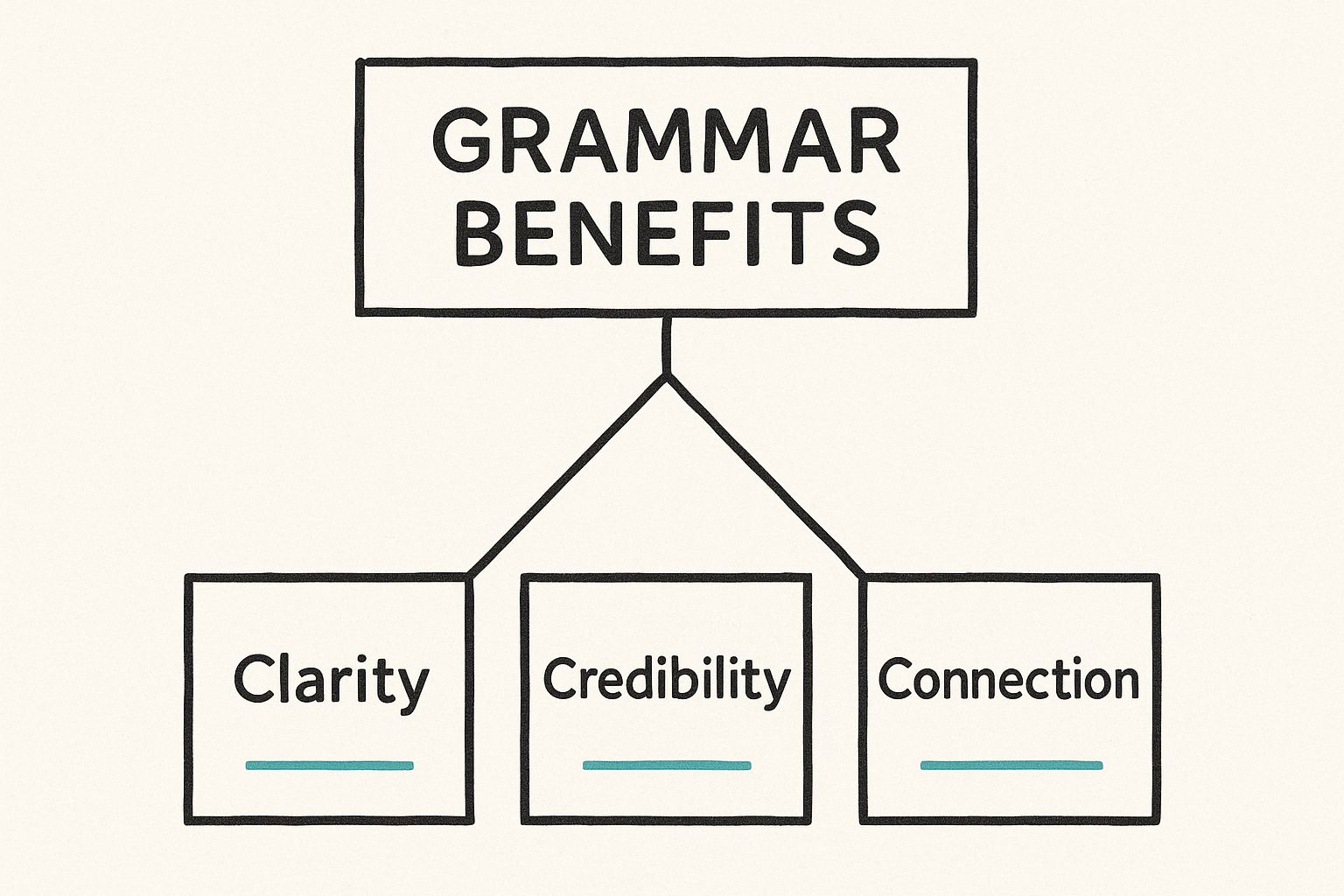
As you can see, clarity, credibility, and connection aren't just buzzwords; they're the direct result of applying basic grammar rules well.
Ethical AI and Authentic Writing
Here at PureWrite, we see AI as a writing partner, not a replacement for the writer. Let AI generate a first draft, but the real magic happens when you step in to refine, polish, and humanize it. This is where your grammar knowledge becomes your secret weapon for creating authentic content.
"Authenticity is the bedrock of trust. Your unique voice, guided by a solid understanding of grammar, is what will make your content stand out and feel genuine to your readers."
Knowing the rules lets you look at AI-generated text with a critical eye. You can catch awkward phrasing, fix subtle errors, and ensure the final piece sounds like you. Even the best tools can produce content that feels robotic, a major red flag for readers and detection software. For more on this, check out our guide on how Turnitin detects AI content.
Ultimately, your goal is to create writing that feels like it was written by a person, for a person. That's exactly what we designed PureWrite to do—help you transform stiff, mechanical text into something natural and engaging. Try PureWrite today to humanize your AI content.
Building Strong Sentences from the Ground Up
Think of sentences as the framing of a house. Without a solid structure, the entire building is weak. In the same way, your writing needs strong, well-built sentences to hold your ideas together and guide your reader clearly from one point to the next.
At its core, every complete sentence has two essential parts: a subject and a predicate. The subject is who or what the sentence is about, and the predicate tells us what the subject is doing or being.
Take this simple example: "The content creator writes." The subject is "The content creator," and the predicate is "writes." This powerful duo forms a complete thought, the most fundamental unit of communication.
The Anatomy of a Sentence
Once you can spot the main components of a sentence, you gain incredible control over your writing. It’s like a mechanic knowing an engine's parts; you can diagnose problems and make everything run smoothly. Let's break down the key players.
- Subject: This is your main character—the person, place, or thing performing the action (e.g., The marketer).
- Verb (Predicate): This is the action itself (e.g., launched).
- Object: This is what receives the action of the verb (e.g., the new campaign).
Put them all together, and you get a crisp, clear statement: "The marketer launched the new campaign." This simple Subject-Verb-Object pattern is the backbone of millions of sentences in English.
Exploring the Four Sentence Types
Writing that uses the same sentence structure over and over quickly becomes dull. To keep your readers hooked, you need to mix things up. Learning to use the four main sentence types lets you control the tone and rhythm of your work, making it far more dynamic.
Imagine a blog post made up of nothing but flat statements—it would be a slog to get through. But by sprinkling in well-placed questions or an emphatic command, you suddenly involve the reader and create a better experience.
A well-crafted sentence does more than just state a fact; it sets a tone, asks a question, gives a command, or expresses emotion. Choosing the right sentence type is the first step in shaping your reader's experience.
Here’s a quick look at the four sentence types and what they do.
The Four Sentence Types Explained
Understanding these distinct functions helps you pick the right tool for the job every time.
| Sentence Type | Purpose | Example | Ends With |
|---|---|---|---|
| Declarative | Makes a statement or states a fact. | "Good grammar improves credibility." | Period (.) |
| Interrogative | Asks a direct question. | "Did you check the article for errors?" | Question Mark (?) |
| Imperative | Gives a command or makes a request. | "Proofread your email before sending." | Period (.) or Exclamation Mark (!) |
| Exclamatory | Expresses strong emotion or excitement. | "Our campaign was a huge success!" | Exclamation Mark (!) |
By consciously mixing these four types, you can make your writing feel more conversational and engaging.
Demystifying Clauses and Phrases
Ready to build more interesting sentences? Let's talk about clauses and phrases. A clause is a group of words with both a subject and a verb, while a phrase is missing one of those key ingredients.
An independent clause is a complete thought that can stand alone: "The writer finished the draft." A dependent clause has a subject and verb but can't stand alone; it leans on the rest of the sentence for meaning: "because the deadline was near."
Combine them, and you get a more complex, informative sentence: "The writer finished the draft because the deadline was near." Learning how to weave these together is fundamental to leveling up your writing, which is a big part of how to improve English writing skills.
Using a tool like PureWrite can help you spot clunky sentence structures and find more graceful alternatives. Our platform analyzes your text and gives you suggestions for varying sentence length and complexity, ensuring your final piece is not only correct but also compelling.
Putting the Eight Parts of Speech to Work
If sentences are the blueprint for your writing, the parts of speech are the tools you use to build them. Getting a handle on these eight core tools isn't about memorizing rules; it's about gaining the power to build your message with precision and style.
Think of it like being a chef. You need to know what the salt does, how the acid cuts through fat, and when to add spice. The parts of speech work the same way—each one brings a distinct and necessary flavor to your sentences.
Nouns and Pronouns: The Main Characters
At the heart of every sentence are your nouns. They name the people, places, things, or ideas you're discussing, like a client, a strategy, or growth. They’re the solid ground your ideas are built on.
Pronouns are handy stand-ins that keep you from sounding repetitive. Instead of saying, "The analyst sent the analyst's report," you can smooth it out: "She sent her report." It just flows better.
Verbs: The Engine of the Sentence
Every complete sentence has a verb. It’s the engine that powers the whole thing forward, telling us what the subject is doing or what it is. Without a verb, a sentence is just a cluster of words going nowhere.
Verbs are incredibly dynamic. They can show assertive action (the team launched the campaign) or a simple state of being (the feedback is positive). For a closer look, check out our guide on action verbs vs. linking verbs.
Adjectives and Adverbs: The Details That Add Color
This is where writing really starts to come to life. Adjectives and adverbs are your descriptive words, adding texture and detail that turn a bland statement into something your reader can actually picture.
- Adjectives add detail to nouns and pronouns. They answer questions like "which one?" or "what kind?" Think a strategic plan or the final draft.
- Adverbs add detail to verbs, adjectives, or even other adverbs. They tell us "how?" or "when?" For example, he spoke confidently, or the results were incredibly strong.
Using them well separates good writing from great writing, ensuring your descriptions feel authentic, not just algorithmically inserted.
Prepositions and Conjunctions: The Connectors
If nouns and verbs are the bricks, prepositions and conjunctions are the mortar holding it all together. They create relationships between words and guide your reader from one idea to the next without any bumps in the road.
Prepositions show how a noun or pronoun relates to something else in the sentence, often dealing with time or location. Words like in, on, at, and before are common prepositions. For example, "The team meets on Friday at the main office."
Conjunctions, on the other hand, are the bridges that join words, phrases, or entire clauses. The most common are for, and, nor, but, or, yet, and so (FANBOYS). They’re essential for building more complex, flowing sentences.
"Understanding how to connect ideas is crucial. Choosing 'but' instead of 'and' can completely pivot the meaning of your sentence and the entire direction of your argument."
Interjections: The Bursts of Emotion
Last but not least, we have interjections. These are quick, emotional exclamations like Wow!, Oops!, or Phew! You won't see them much in a formal report, but they’re fantastic for conversational pieces like blog posts.
A well-placed Yikes! can add a jolt of personality and relatability that AI-generated text often misses. It’s one of those small, humanizing touches that can make a big difference in connecting with your reader.
Getting Punctuation and Capitalization Right

Think of punctuation as the traffic signals for your writing. These little marks tell your reader when to slow down, when to stop, and when an idea needs special attention. Getting them right is crucial if you want to be understood clearly.
Capitalization works in a similar way. It’s not just for the beginning of a sentence—it’s a powerful tool for signaling importance and adding a professional sheen. When you nail both, you make your work far more credible and effective.
Mastering the Most Common Punctuation Marks
Let’s be honest, a few punctuation marks cause more trouble than others, even for seasoned writers. Instead of dry definitions, we'll look at how they work in the real world so you can use them confidently.
Commas (,): The comma is easily the most versatile—and most misused—mark. Its main job is to create small pauses and separate different ideas within a sentence.
- Separating items in a list: We need to write the blog post, create the graphics, and schedule the social media promotion.
- Joining two full sentences with a conjunction: The first draft was good, but the final version was even better.
- Setting off an introductory thought: After reviewing the analytics, we decided to change our strategy.
Semicolons (;): A semicolon is like a "super-comma," creating a pause that’s stronger than a comma but not as final as a period. It's the perfect tool for connecting two closely related sentences.
- Example: AI can generate content quickly; human writers add the necessary creativity and nuance.
Apostrophes ('): Apostrophes have two distinct jobs: showing ownership or standing in for missing letters in contractions. Confusing them is a common trip-up.
- Possession: The writer's style was unique. (One writer) The writers' styles were unique. (Multiple writers)
- Contractions: It's (it is) a common mistake. They're (they are) reviewing the document.
Correct punctuation isn’t just a technical detail—it’s a sign of respect for your reader. It clarifies your message, prevents confusion, and shows a commitment to quality that builds trust with every sentence.
Capitalization Rules That Polish Your Writing
Everyone knows to capitalize the first word of a sentence, but professional writing demands more attention to detail. Consistent, correct capitalization in titles, headings, and names makes your content look polished and authoritative. For instance, in business communications, getting capitalization right is essential, as we cover in our guide on how to write professional emails.
Key Capitalization Scenarios
Beyond the first word of a sentence, here are the most important capitalization rules to keep in mind.
- Proper Nouns: Always capitalize the specific names of people, places, companies, and brands. Think Sarah, New York City, and Google.
- Titles and Headings: Capitalize the first word and all "major" words (nouns, verbs, adjectives). Little words like a, an, the, and, and but stay lowercase unless they are the first word.
- Days, Months, and Holidays: These are always capitalized, like Monday, October, or Thanksgiving. Seasons, however, are a different story; winter and summer aren't capitalized unless part of a formal name, like the "Winter Olympics."
Mastering these foundational rules will instantly elevate the quality of your writing. When you’re trying to refine an AI-generated draft, these are often the exact details that require a human touch to get right.
Common Grammar Traps and How to Avoid Them
Even the best writers have blind spots. When you're in the creative flow, it's easy to let a few common errors slip past, especially on a tight deadline. Think of your final proofread as the last line of defense for your credibility.
Let’s be honest, many of these slip-ups happen when we're writing fast or trusting a grammar checker too much. Here are some of the most common grammar traps and how you can train your eye to catch them every time.
Subject-Verb Agreement Errors
This is a classic. The rule is simple: a singular subject takes a singular verb, and a plural subject takes a plural verb. But in practice, especially in longer sentences, things can get messy.
- Incorrect: The box of old photographs are in the attic.
- Correct: The box of old photographs is in the attic.
The real subject here isn't "photographs," it's the singular "box." A go-to trick is to mentally cross out the phrase between the subject and the verb. "The box... is in the attic." Suddenly, it becomes obvious.
Pesky Dangling Modifiers
Dangling modifiers are phrases that accidentally describe the wrong thing in a sentence, often with hilarious results. They create confusion and can instantly tank your professional tone.
A modifier is like a spotlight—it needs to shine directly on the word it’s describing. When it's left "dangling," that spotlight points somewhere else entirely, leaving your reader wondering what's going on.
- Confusing: Rushing to finish the report, the printer jammed. (This makes it sound like the printer was rushing).
- Clear: While I was rushing to finish the report, the printer jammed.
To fix these, just make sure the subject of your main sentence is the one actually doing the action described in the opening phrase.
Homophones: Their, There, and They're
Ah, homophones. These are words that sound alike but have different meanings and spellings. They’re notorious because your spell-checker won't flag them as an error if you’ve simply used the wrong one. Nailing these is a small detail that signals you’re a careful writer.
Here's a quick way to remember them:
- Their: Shows possession or ownership. (Is that their car?)
- There: Points to a location or place. (Let's meet over there.)
- They're: Just a shorter way of saying "they are." (They're going to be late.)
Before you hit publish, it's worth taking a moment to review these common mix-ups. A quick scan can save you from an embarrassing mistake.
Quick Fixes for Common Grammar Goofs
Here’s a little cheat sheet to help you spot and fix these common goofs.
| Common Mistake | Corrected Example | Quick Tip |
|---|---|---|
| The team of developers are working late. | The team of developers is working late. | Is the true subject "team" (singular) or "developers"? Focus on the main noun. |
| Having finished the project, the celebration began. | After we finished the project, the celebration began. | Ask yourself: Who finished the project? Make sure that person is the subject. |
| Your going to do great! | You're going to do great! | Read it out loud as "You are." If it makes sense, you need "you're." |
| I have less books than you. | I have fewer books than you. | Use "fewer" for things you can count (books) and "less" for things you can't (water). |
Taking an extra minute to double-check for these specific errors can make a huge difference in how polished and professional your writing feels to the reader.
Bending the Rules for Style
Now, not every "rule" you learned in school is sacred. Some are more like style guidelines. Take the old warning to never start a sentence with "And" or "But." That's often more about stiff tradition than what makes for good, engaging writing.
In fact, some of the greats have been doing it for centuries. Novelist Henry James, for example, started sentences with "And" more than 1,900 times per million words. You can dig into fascinating data on these so-called rules through linguistic research from the University of Pennsylvania.
The real key is to understand the rule before you decide to break it intentionally. Kicking off a sentence with a conjunction can add rhythm, create emphasis, or make your writing feel more conversational. It's a powerful tool, especially for blog posts and marketing content.
If you've used AI to generate a first draft and it feels a bit robotic, a tool like PureWrite can help. Our platform is built to humanize AI-generated text, smoothing out awkward phrasing and injecting that natural flow that connects with real people. It helps give your writing the authentic touch it needs.
Applying Grammar Rules in the Digital Age
https://www.youtube.com/embed/JXlQyps99Ts
Grammar isn't a stuffy set of rules from a dusty old textbook. Think of it more as a living tool that changes with how we communicate. In a world dominated by instant messages, blogs, and social media, good grammar has taken on a new role.
It’s no longer just about being "correct." The real goal now is readability and engagement. This means you have to be smart about your writing—breaking up long paragraphs, using bullet points, and adopting a more direct, conversational style. If you want to grab and hold someone's attention online, your writing has to be sharp and clear.
Finding the Right Balance for Online Writing
So, how do you sound credible online without sounding like a robot? The trick is knowing which grammar rules are non-negotiable and which ones you can bend for effect.
For instance, you'd never use a sentence fragment in a formal business report. But in a blog post? A well-placed fragment can add serious punch. It all comes down to matching your writing style to the platform and, most importantly, to your audience.
The fast-paced nature of digital communication has even birthed its own conventions. Acronyms like LOL and the entire universe of emoji have become standard ways to inject tone. This evolution means writers today have to be nimble, balancing traditional standards with these new digital norms. You can dig deeper into these emerging grammar trends on fiveable.me.
"The best digital writing feels like a conversation. It’s not about abandoning grammar but about using it skillfully to connect with your reader on a human level."
Practical Tips for Digital Readability
To make your content really pop, zero in on clarity and structure. Here are a few simple ways to apply grammar rules in a way that resonates today:
- Embrace short paragraphs: Keep them to just one to three sentences. This creates valuable white space on the screen, making your content feel much less overwhelming to read.
- Use lists strategically: Bullet points and numbered lists are your best friends. They break up walls of text and let readers scan for the most important takeaways in a flash.
- Write for human connection: AI can churn out words, but it often misses that natural, conversational rhythm. When you're editing, always ask yourself: "Does this sound like something a real person would say?"
If your AI-generated drafts feel a little stiff, you're not alone—it's a common problem. That's why we built PureWrite. To learn how to polish that robotic text, check out our guide on how to rewrite AI text to sound more human. Give PureWrite a try to see how easily you can make your writing truly connect with people.
Let's Tackle Your Biggest Grammar Head-Scratchers
Even the most seasoned writers get tripped up by a few tricky grammar rules. Let's clear the air on some of the most common questions that pop up, so you can put these debates to rest and write with confidence.
Can You Really Start a Sentence with 'And' or 'But'?
Let's get this one out of the way: yes, you absolutely can. Many of us had it drilled into our heads in school that this was a major writing sin, but it's a myth that's long overdue for busting.
Starting a sentence with a conjunction like "and" or "but" is a powerful stylistic tool. And it’s used by professional writers all the time to make their writing sound more conversational and create a natural, flowing rhythm between thoughts.
Think about it. When you speak, you start sentences this way without a second thought. Bringing that same cadence into your writing can be incredibly effective for adding emphasis or creating a dramatic pause.
The trick is to do it on purpose, not by accident. A sentence that kicks off with "But" can introduce a surprising twist or a strong counter-argument that immediately pulls the reader in.
What About Ending a Sentence with a Preposition?
This is another one of those zombie rules that just won't die. The notion that you can't end a sentence with a preposition (words like of, to, with, for) is an outdated guideline that often makes sentences sound stuffy and unnatural.
Which of these sounds better to you?
- Stiff and formal: From where did you come?
- Natural and clear: Where did you come from?
The second one wins every time. It’s how real people talk, and it’s perfectly correct. Remember, the ultimate goal of good writing is clarity, not clinging to ancient rules that twist your sentences into knots.
Nailing these basic grammar rules is a huge step, but making your writing truly connect with readers goes beyond just being correct. If you're looking to breathe life into dry, robotic AI drafts, we can help. Give PureWrite a try and see how it humanizes your content with a single click.